Main uses of biological databases
- Search data
- Download data
- Data analysis using integrated tools
- Submit data
Module 3: data management
Ifremer (Plouzané)
INRAE (Rennes)
2026-01-06
=> FAIR (Findable Accessible Interoperable Reusable) context!
image from https://digitalworldbiology.com/sites/default/files/DWB%20Product/teaser-images/exploring_databases.png
Specialists : databases that specialize in a particular organism or a particular type of data.
Primary biological databases : data that it derives experimentally
Data : original and curated data
Raw experimental data
Purposes : data deposition and curation
Sources : researchers and laboratories
Original formats (fasta, fastq …)
Frequent updates and additions
Examples: GenBank (NCBI), EMBL-EBI, DDBJ (DNA Data Bank of Japan)
Secondary biological databases : data obtained by analysis or treatment of data present in primary database
Data : derived data
Processed and annotated data
Purposes : data integration and analysis
Sources : primary databases
Standardized formats (GFF, BED …)
Updates based on primary databases
Examples : KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomics), Pfam (Protein Families), SCOP (Structural Classification Of Proteins)
=> FAIR PRINCIPLES!
=> Databases are essential tools for managing and utilizing data effectively in various fields and applications
A text-based format for representing either nucleotide sequences or amino acid (protein) sequences
>MU105551.1 Sinapis alba strain S2 GC0560-79 unplaced genomic scaffold Sina_scaffold1, whole genome shotgun sequence
TGCATCAAAGATATTACCCTTGTGAGCTGGTGTAAGCTCACCGAGACGTACCGAGATCACGTTGATCTTGGGAACTCGTA
TATCTTGGTGTTCTTAAATTTCTGCACATCATCAAACACAAATCTAACTCAGCACAAATAAACACAACATCTGCAATCTG
AATCACATCAGAATTGAATACAAGAACATAAAACcaacacaaaaaacaaaagttagagactttttggtttcttcaagttt
ttttCAAAGAGAGAAGGGCTAAATAAAACGTACGTGGCCATCAGGGTTTCCTGATTGCTCCCAGTAGAGTGTGTGAGTATA text-based format for storing both a biological sequence (usually nucleotide sequence) and its corresponding PHRED quality scores
@A00514:914:HTC5YDRXY:1:1101:4851:1031 1:N:0:GTATTCCACC+TTGTCTACAT
TNGTCGTTGAGCTTGGACTTGACCAGCGGGAAGTCGGACGACGACAGACGGCGGCCGTCTTTGGTGCATGTCCTCAGCACACGTTCCTCCCACGTCTGCGG
+
F#FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF:FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
@A00514:914:HTC5YDRXY:1:1101:4517:1047 1:N:0:GTATTCCACC+TTGTCTACAT
AGTCCGTTGATGCAGTAAATACTTGCCAACAAGCATCCCGGTAGTCCAATGAAATAGGTCACTTTCTTCCACAATGACAGACCTTGGAGGACCTCGGGTGA
+
,F,FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF::F:FFFFFFFFFFFFF,F,FFFFFFFFFFF:FFFFFFF:FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF:F,FF:FFFFFF,FFFFA text-based format for storing sequences and their associated meta-information, feature coordinates, and annotations
One sequence entry starts with an identifier line (“ID”), followed by further annotation lines. The start of the sequence is marked by a line starting with “SQ” and the end of the sequence is marked by two slashes (“//”).
Example from wiki.biouml.org
ID ADHBADA2 standard; DNA; VRT; 1145 BP.
XX
AC J00923; J00924;
XX
DT 13-JUN-1985 (Rel. 06, Created)
DT 22-NOV-1994 (Rel. 41, Last updated, Version 2)
XX
DE Duck alpha-A-globin gene and 5' flank.
XX
KW alpha-globin; globin.
XX
OS Cairina moschata (duck)
OC Eukaryota; Animalia; Metazoa; Chordata; Vertebrata; Aves;
OC Neornithes; Neognathae; Anseriformes; Anatidae.
XX
RN [1]
RP 603-696
RX MEDLINE; 83028533.
RA Niessing J., Erbil C., Neubauer V.;
RT "The isolation and partial characterization of linked alpha-A- and
RT alpha-D-globin genes from a duck DNA recombinant library";
RL Gene 18:187-191(1982).
XX
RN [2]
RP 1-1145
RX MEDLINE; 83158759.
RA Erbil C., Niessing J.;
RT "The complete nucleotide sequence of the duck alpha-A-globin
RT gene";
RL Gene 20:211-217(1982).
XX
DR EPD; 33033; Cm a'A-globin.
DR SWISS-PROT; P01987; HBA_CAIMO.
XX
CC The alpha-A-globin gene is linked to the alpha-D-globin gene. [1]
CC compared their alpha-A-globin gene sequence with chicken alpha-A-
CC and alpha-S-globin gene sequences, as well as with other avian and
CC mammalian alpha-A-globin gene sequences. NCBI gi: 212911
XX
FH Key Location/Qualifiers
FH
FT source 1..1145
FT /organism="Cairina moschata"
FT prim_transcript 331..1145
FT /note="alpha-A-globin mRNA"
FT CDS join(367..461,612..816,921..1049)
FT /note="alpha-A globin; NCBI gi: 212914"
FT /codon_start=1
FT exon 367..461
FT /note="alpha-A globin"
FT /number=1
FT intron 462..611
FT /note="alpha-A-globin intron A"
FT exon 612..816
FT /number=2
FT intron 817..920
FT /note="alpha-A-globin intron B"
FT exon 921..>1049
FT /note="alpha-A globin"
FT /number=3
XX
SQ Sequence 1145 BP; 193 A; 435 C; 291 G; 226 T; 0 other;
ctcatgctgg ggttgcctcc ccccctcaaa ccctaacctt aatcccatct cgtgctgggg 60
tcagaccccc ctaaccctaa cccagttcat gccgggatca gcccccccaa accctaaccc 120
taaacccatc tcgtgccggg gtcagacccc ccccaaccct aaccccgacc ccagttcatg 180
ccggggtcgc ccccccccgg tggtgccggt gccgcaggcg gggcagggcg gcggccccgc 240
ctggccgagg tccagccgcg acggggcggg cggggcgggg cggcgcccgg gccggcacgg 300
ggatataagg ccggcggcac cagtgggggc acccgtgctg ggggctgcca acgcggagct 360
gcaaccatgg tgctgtctgc ggctgacaag accaacgtca agggtgtctt ctccaaaatc 420
ggtggccatg ctgaggagta tggcgccgag accctggaga ggtaggtgtc tgtccccgtc 480
ctttgtccgt ccctgatcct ctcctctcta accccatgct ctcccccacc ataactgtcc 540
gtgtcctacc ccaccccatc catcccccct gtccgttgat cccgctggcc ctgactcgct 600
ctgctccaca ggatgttcat cgcctacccc cagaccaaga cctacttccc ccactttgac 660
ctgcagcacg gctctgctca gatcaaggcc catggcaaga aggtggcggc tgccctagtt 720
gaagctgtca accacatcga tgacattgcg ggtgctctct ccaagctcag tgacctccac 780
gcccaaaagc tccgtgtgga ccctgtcaac ttcaaagtga gtctggtgac tccccccagc 840
tcctcttcag cacccatcct gggccatccg gccacccctt tacctccccc actcgctcac 900
cgtctccttt tgcctttcag ttcctgggcc actgcttcct ggtggtggtt gccatccacc 960
accccgctgc cctgacccca gaggtccacg cttccctgga caagttcatg tgcgccgtgg 1020
gtgctgtgct gactgccaag taccgttaga cggcaccgtg gctagagctg gacccaccct 1080
gttgccagcc ttccaactgc aagcagccaa atgatctgaa ataaaatctg ttgcatttgt 1140
gctcc 1145
//
A text-based format for storing sequences and their associated meta-information, feature coordinates, and annotations
LOCUS JN835270 1574 bp mRNA linear INV 07-JUL-2015
DEFINITION Spodoptera litura putative olfactory receptor 3 (OR3) mRNA,
complete cds.
ACCESSION JN835270
VERSION JN835270.2
KEYWORDS .
SOURCE Spodoptera litura
ORGANISM Spodoptera litura
Eukaryota; Metazoa; Ecdysozoa; Arthropoda; Hexapoda; Insecta;
Pterygota; Neoptera; Endopterygota; Lepidoptera; Glossata;
Ditrysia; Noctuoidea; Noctuidae; Amphipyrinae; Spodoptera.
REFERENCE 1 (bases 1 to 1574)
AUTHORS Lin,X., Zhang,Q., Wu,Z. and Du,Y.
TITLE Identification and Differential Expression of a Candidate Sex
Pheromone Receptor in Natural Populations of Spodoptera litura
JOURNAL PLoS ONE 10 (6), E0131407 (2015)
PUBMED 26126192
REMARK Publication Status: Online-Only
REFERENCE 2 (bases 1 to 1574)
AUTHORS Wu,Z.N., Du,Y.J. and Zhuge,Q.C.
TITLE Two olfactory receptors from Spodptera litura
JOURNAL Unpublished
REFERENCE 3 (bases 1 to 1574)
AUTHORS Wu,Z.N., Du,Y.J. and Zhuge,Q.C.
TITLE Direct Submission
JOURNAL Submitted (10-OCT-2011) Institute of Health and Environment,
Wenzhou Medical College, University-Town, Wenzhou, Zhejiang 325035,
China
REFERENCE 4 (bases 1 to 1574)
AUTHORS Wu,Z.N., Du,Y.J. and Zhuge,Q.C.
TITLE Direct Submission
JOURNAL Submitted (26-MAR-2012) Institute of Health and Environment,
Wenzhou Medical College, University-Town, Wenzhou, Zhejiang 325035,
China
REMARK Sequence update by submitter
COMMENT On Mar 26, 2012 this sequence version replaced JN835270.1.
FEATURES Location/Qualifiers
source 1..1574
/organism="Spodoptera litura"
/mol_type="mRNA"
/db_xref="taxon:69820"
gene 1..1574
/gene="OR3"
/note="SlitOR3"
CDS 67..1365
/gene="OR3"
/codon_start=1
/product="putative olfactory receptor 3"
/protein_id="AEY84943.2"
/translation="MGLKKFLFEDESVQGITAPTDYLYVKLLRMTLRIIATWPQTELG
EKEPVYLNVFLKYFYLVATIGCQIGSYCYLRTYSDELTMMEAGHNYIMIMMTFIDISR
ITSLTFSTEYRKLCKEFFTKMHLFYFKDISEHAMATHKRVHLISHLFTLWLLFQMLFG
VPLFNLVPMYYNYAAGRYKPGGTQNSTFEHSMYYQYPFDTLTEIKGYIVANIINWILS
SLCVIWFCMCDLILLLMVFNIWGHLRMLTYTLNNFPRPSVETTITIDGGLTVTSAIYS
DEENVQIFRKLKECVDYHRRIVEFNSKVSDVFGPMLIIYYLYHQTSGCLLLLECSQMT
APVLMRYLPLTIVCTRQLIQLSVIFELIGTESEKLPSAVYSVPWECMSISNKKFVIFF
LMNVKEPIAVKPPGIANVGVTTMASILRTSLSYFTFLRSI"
ORIGIN
1 atggacaccc ttcagaagat atgcagatag aactttagat gtaaattact gattttcttc
61 gcaaagatgg gtttaaaaaa gtttcttttt gaagatgaat ctgtgcaggg catcactgca
121 ccaactgatt acctctacgt taaactcttg cgcatgactt tgcgtatcat cgccacctgg
181 cctcagacag aactcggaga gaaggaacct gtgtacttga atgtttttct aaagtatttt
241 tatttggtag ccaccattgg ctgtcaaatc ggttcatatt gttacctcag aacgtatagt
301 gatgaactta ccatgatgga ggctggtcat aattatatta tgattatgat gacattcatc
361 gatatatcaa gaattacatc gctcacattt tctacggaat acagaaaact ttgcaaagaa
421 ttcttcacga aaatgcatct cttctatttc aaagatatat ctgaacatgc gatggcgact
481 cacaaacggg tgcacttgat atctcatttg tttactttgt ggttattatt tcaaatgctg
541 tttggggtgc ctctttttaa cctcgtacca atgtactata attatgctgc tggaagatat
601 aaacctggtg gcacacaaaa ctcaactttt gaacattcta tgtattacca gtatccattt
661 gatacgctca ctgaaataaa gggatatatc gttgctaata ttattaattg gatattgtct
721 tctctctgcg taatctggtt ttgcatgtgt gacctcattc tattactgat ggtgttcaat
781 atttggggac atttgagaat gcttacatac accctgaata attttcctag gccaagtgta
841 gagactacta tcacaataga tggaggatta acagtaacaa gtgctatata ttctgatgaa
901 gagaacgtac aaatatttag aaagttaaaa gaatgtgttg attatcatcg acggattgtt
961 gaatttaata gcaaagtttc tgatgtattt ggtccaatgt tgatcatcta ttatttatac
1021 catcaaacaa gcggctgttt attgttactg gagtgttcac aaatgactgc accagtccta
1081 atgcgttatt tacccctgac gatagtgtgc actcggcaac tgattcagtt atcagtaatt
1141 tttgaactaa ttggaactga gagcgaaaag ttaccaagcg ccgtgtacag tgtaccatgg
1201 gaatgtatga gcataagtaa taaaaaattt gtgatattct tcttgatgaa tgttaaagag
1261 ccaatagctg tgaaacctcc tggcattgcc aatgttggtg tcacgacaat ggcttcgatt
1321 ttgagaacat cgttgtccta tttcaccttc ttacgcagca tttgaattta tgactttcta
1381 aacaactatc tctcaaatca tctctcacga gttttgtcaa gttttctcac aaattatcac
1441 actatattta tgctaacagt taaatgtaaa aatgttaata ataatgaata tgtttgctat
1501 gaaatagttt atcaccaatt gttttatatt gtttcaataa attctgacgt cacaaaaaaa
1561 aaaaaaaaaa aaaa
//A text-based for describing genes and other features of DNA, RNA and protein sequences (annotation)
##gff-version 3
HiC_scaffold_1 AUGUSTUS gene 7086 9916 0.14 + . ID=g14228
HiC_scaffold_1 AUGUSTUS mRNA 7086 9916 0.14 + . ID=g14228.t1;Parent=g14228
HiC_scaffold_1 AUGUSTUS five_prime_UTR 7086 7230 0.21 + . ID=g14228.t1.5UTR1;Parent=g14228.t1
HiC_scaffold_1 AUGUSTUS exon 7086 7405 . + . ID=g14228.t1.exon1;Parent=g14228.t1
HiC_scaffold_1 AUGUSTUS CDS 7231 7405 0.84 + 0 ID=g14228.t1.CDS1;Parent=g14228.t1
HiC_scaffold_1 AUGUSTUS CDS 8821 8930 0.99 + 2 ID=g14228.t1.CDS2;Parent=g14228.t1
HiC_scaffold_1 AUGUSTUS exon 8821 8930 . + . ID=g14228.t1.exon2;Parent=g14228.t1
HiC_scaffold_1 AUGUSTUS CDS 8999 9190 1 + 0 ID=g14228.t1.CDS3;Parent=g14228.t1
HiC_scaffold_1 AUGUSTUS exon 8999 9190 . + . ID=g14228.t1.exon3;Parent=g14228.t1
HiC_scaffold_1 AUGUSTUS CDS 9761 9883 1 + 0 ID=g14228.t1.CDS4;Parent=g14228.t1
HiC_scaffold_1 AUGUSTUS exon 9761 9916 . + . ID=g14228.t1.exon4;Parent=g14228.t1
HiC_scaffold_1 AUGUSTUS three_prime_UTR 9884 9916 0.4 + . ID=g14228.t1.3UTR1;Parent=g14228.t1Identical to GFF, version 2
HiC_scaffold_1 AUGUSTUS exon 7086 7230 . + . ID 1 ; gene_biotype protein_coding ; gene_id "g14228.t1" ; transcript_id "g14228.t1" ;
HiC_scaffold_1 AUGUSTUS exon 7231 7405 . + 0 ID 1 ; gene_biotype protein_coding ; gene_id "g14228.t1" ; transcript_id "g14228.t1" ;
HiC_scaffold_1 AUGUSTUS exon 8821 8930 . + 2 ID 1 ; gene_biotype protein_coding ; gene_id "g14228.t1" ; transcript_id "g14228.t1" ;
HiC_scaffold_1 AUGUSTUS exon 8999 9190 . + 0 ID 1 ; gene_biotype protein_coding ; gene_id "g14228.t1" ; transcript_id "g14228.t1" ;
HiC_scaffold_1 AUGUSTUS exon 9761 9883 . + 0 ID 1 ; gene_biotype protein_coding ; gene_id "g14228.t1" ; transcript_id "g14228.t1" ;
HiC_scaffold_1 AUGUSTUS exon 9884 9916 . + . ID 1 ; gene_biotype protein_coding ; gene_id "g14228.t1" ; transcript_id "g14228.t1" ;A text file used to store genomic regions as coordinates and associated annotations
chr7 127471196 127472363 Pos1 0 + 127471196 127472363 255,0,0
chr7 127472363 127473530 Pos2 0 + 127472363 127473530 255,0,0
chr7 127473530 127474697 Pos3 0 + 127473530 127474697 255,0,0
chr7 127474697 127475864 Pos4 0 + 127474697 127475864 255,0,0
chr7 127475864 127477031 Neg1 0 - 127475864 127477031 0,0,255
chr7 127477031 127478198 Neg2 0 - 127477031 127478198 0,0,255
chr7 127478198 127479365 Neg3 0 - 127478198 127479365 0,0,255
chr7 127479365 127480532 Pos5 0 + 127479365 127480532 255,0,0
chr7 127480532 127481699 Neg4 0 - 127480532 127481699 0,0,255A standard text file format for storing gene sequence variations
#CHROM POS ID REF ALT QUAL FILTER INFO FORMAT NA00001 NA00002 NA00003
20 14370 rs6054257 G A 29 PASS NS=3;DP=14;AF=0.5;DB;H2 GT:GQ:DP:HQ 0|0:48:1:51,51 1|0:48:8:51,51 1/1:43:5:.,.
20 17330 . T A 3 q10 NS=3;DP=11;AF=0.017 GT:GQ:DP:HQ 0|0:49:3:58,50 0|1:3:5:65,3 0/0:41:3
20 1110696 rs6040355 A G,T 67 PASS NS=2;DP=10;AF=0.333,0.667;AA=T;DB GT:GQ:DP:HQ 1|2:21:6:23,27 2|1:2:0:18,2 2/2:35:4
20 1230237 . T . 47 PASS NS=3;DP=13;AA=T GT:GQ:DP:HQ 0|0:54:7:56,60 0|0:48:4:51,51 0/0:61:2
20 1234567 microsat1 GTC G,GTCT 50 PASS NS=3;DP=9;AA=G GT:GQ:DP 0/1:35:4 0/2:17:2 1/1:40:3A text-based format originally for storing biological sequences aligned to a reference sequence
D00562:237:CBFBNANXX:5:2307:15276:42153 1187 HiC_scaffold_1 375 3 12M292N112M = 803 745 CACAGAGGCTGTCACAATCTACGTTCCCCAGTAAGTCGGCGGCGGAGCTGTCTCGACTGGAGCCGTGTACGTCAGTAGCGGGCATGGAGCTATGGTCGCAGTGCTACGAGCGCTGGCTCGTGCC CBCCCGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGCGGGGGGGGGGGGFEGGGGFGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGAGGGGGGGGG
MD:Z:124 PG:Z:MarkDuplicates RG:Z:T1_S15 NH:i:2 HI:i:2 NM:i:0 AS:i:250 XS:A:+
D00562:237:CBFBNANXX:5:1306:14559:55311 1187 HiC_scaffold_1 375 3 12M292N112M = 806 745 CACAGAGGCTGTCACAATCTACGTTCCCCAGTAAGTCGGCCGCGGAGCTGTCTCGACTGCAGCCGTGTACGGCAGTAGCGGGCATGGAGCTATGGTCGCAGTGCTACGAGCGCTGGCGCGTGCC 33AA0;1;/?E;11E1CGGCG:FB111FGG/<>11>1EEG/<E///</1::?EG1>EGG0:E>0=/9>FG0//<900DEGG/DGGGGGG<//EG/;EG.>6.////:C..96CG.C....69..
MD:Z:40G18G11T45T6 PG:Z:MarkDuplicates RG:Z:T1_S15 NH:i:2 HI:i:2 NM:i:4 AS:i:235 XS:A:+
D00562:237:CBFBNANXX:5:1111:19941:76960 163 HiC_scaffold_1 375 3 12M292N112M = 803 745 CACAGAGGCTGTCACAATCTACGTTCCCCAGTAAGTCGGCGGCGGAGCTGTCTCGACTGGAGCCGTGTACGTCAGTAGCGGGCATGGAGCTATGGTCGCAGTGCTACGAGCGCTGGCTCGTGCC CCCCCGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGFGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGEGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGGDGGGGGGGGGGG
MD:Z:124 PG:Z:MarkDuplicates RG:Z:T1_S15 NH:i:2 HI:i:2 NM:i:0 AS:i:250 XS:A:+
A compressed binary version of a SAM file that is used to represent aligned sequences up to 128 Mb
=> All these formats are standard, you must use it without modifying it!
EBI website contains 150 databases
ENA (European Nucleotide Archive) : nucleotide sequencing information, covering raw sequencing data, sequence assembly information and functional annotation
ENA (European Nucleotide Archive) : nucleotide sequencing information, covering raw sequencing data, sequence assembly information and functional annotation
Ensembl : genome browser for animal genomes that supports research in comparative genomics, evolution, sequence variation and transcriptional regulation.
Ensembl annotates genes, computes multiple alignments, predicts regulatory function and collects disease data.
Ensembl tools include BLAST, BLAT, BioMart and the Variant Effect Predictor (VEP) for all supported species.
Release 115 (09/2025) : 348 species !
Rfam : collection of RNA families, each represented by multiple sequence alignments, consensus secondary structures and covariance models
Uniprot : high-quality, comprehensive and freely accessible resource of protein sequence and functional information.
AlphaFold : database for protein structure predictions for numerous species
InterProscan : functional analysis of proteins by classifying them into families and predicting domains and important sites
Pfam : A database of conserved protein families and domains. Pfam is a member database of InterPro. The Pfam database is a large collection of protein families, each represented by multiple sequence alignments and hidden Markov models (HMMs)
HMMER : Fast sensitive protein homology searches using profile hidden Markov models (HMMs) for querying against both sequence and HMM target databases.
Biomedical and genomic information
NCBI website contains 58 Databases
Nucleotide Database : A collection of nucleotide sequences from several sources, including :
Searching the Nucleotide Database will yield available results from each of its component databases.
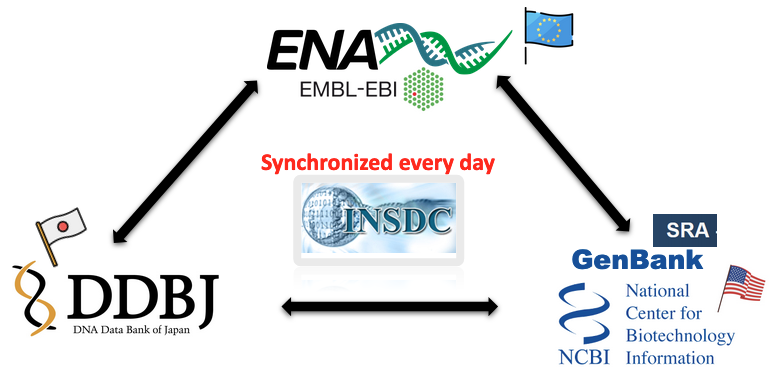
GenBank : an annotated collection of all publicly available DNA sequences, is part of the International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration , which comprises :
- the DNA DataBank of Japan (DDBJ),
- the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL),
- GenBank at NCBI.
GenBank consists of several divisions, most of which can be accessed through the Nucleotide database.
SRA (Sequence Read Archive) : stores sequencing data from the next generation of sequencing platforms including Roche 454 GS System®, Illumina Genome Analyzer®, Life Technologies AB SOLiD System®, Helicos Biosciences Heliscope®, Complete Genomics®, and Pacific Biosciences SMRT®.
Genome : Contains sequence and map data from the whole genomes of over 1000 organisms.
RefSeq : A comprehensive, integrated, non-redundant, well-annotated set of reference sequences including genomic, transcript, and protein.
Protein Database : includes protein sequence records from a variety of sources, including GenPept, RefSeq, Swiss-Prot, PIR, PRF, and PDB.
PubMed : collection of biomedical books that can be searched directly or from linked data in other NCBI databases
Database Commons is a curated catalog of worldwide biological databases, with the aim to provide a full landscape of biological databases throughout the world and enable easy retrieval and access to a specific collection of databases of interest
Banks can be available in different versions and in different index format: fasta, gff, blast, bwa, bowtie, bowtie2, start, diamond, picard,
ls /shared/bank/
COG danio_rerio krona oryza_nivara saccharomyces_cerevisiae
MMSEQS_DB data.galaxyproject.org lachancea_kluyveri oryza_punctata saccharum_spontaneum
PFAM daucus_carota malus_domestica oryza_rufipogon salmonella_typhimurium
README.txt dbcan mgnify oryza_sativa_aus schizosaccharomyces_pombe
_scripts dram mmdb oryza_sativa_basmati software_specific
accession2taxid drosophila_melanogaster motus oryza_sativa_indica solanum_lycopersicum
alphafold2 eggnog-mapper mus_musculus oryza_sativa_japonica sorghum_bicolor
amrfinder elaeis_guineensis musa_acuminata oryza_sativa_nerica squeezemeta
anas_platyrhynchos emapperdb ncbi_taxonomy pdb sus_scrofa
arabidopsis_lyrata equus_caballus neofusicoccum_parvum pfam trypanosoma_brucei
arabidopsis_thaliana escherichia_coli nicotiana_tabacum phalaenopsis_aphrodite uniprot
astyanax_mexicanus felis_catus nr phalaenopsis_equestris uniprot_swissprot
bakta frogs nt phoenix_dactylifera uniref50
bos_taurus galaxy_test-data ophrys_sphegodes phyloflash uniref90
bowtie-index genbank oryctolagus_cuniculus plasmidfinder vanilla_planifolia
candida_glabrata greengenes oryza_barthii populus_trichocarpa vitis_vinifera
canis_lupus_familiaris gtdbtk oryza_brachyantha prunus_persica xenopus_laevis
capra_hircus hhsuite oryza_glaberrima rattus_norvegicus zea_mays
checkm homo_sapiens oryza_glumipatula refseq zymoseptoria_tritici
clostridium_perfringens kraken oryza_longistaminata rosa_chinensis
cocos_nucifera krakenuniq oryza_meridionalis rsat_organismls /shared/bank/uniprot_swissprot/
current uniprot_swissprot_2018-10-10 uniprot_swissprot_2020_03
ls /shared/bank/uniprot_swissprot/current/
blast diamond fasta flat listingv1.blast mapping mmseqsBanks can be available in different versions and in different index format: fasta, gff, blast, bwa, bowtie, bowtie2, start, diamond, picard,
The banks are organized first per species or bank names, then per index:
homo_sapiens/
├── GRCh38
│ ├── bwa
│ │ ├── Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.dna.primary_assembly.fa -> ../fasta/Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.dna.primary_assembly.fa
├── Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.dna.primary_assembly.fa.amb
├── Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.dna.primary_assembly.fa.ann
├── Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.dna.primary_assembly.fa.bwt
├── Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.dna.primary_assembly.fa.pac
└── Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.dna.primary_assembly.fa.sa
│ │ └── ...
│ ├── fasta
│ │ ├── Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.dna.primary_assembly.fa
├── Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.dna.primary_assembly.fa.fai
├── Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.dna.primary_assembly.fa.readme
├── Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.dna.toplevel.fa
├── Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.dna.toplevel.fa.fai
└── Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.dna.toplevel.fa.readme
│ │ └── ...
│ ├── gff3
│ │ ├── Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.94.gff3
│ │ └── Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.94.gff3.readme
│ └── star
│ ├── Genome
│ ├── Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.dna.primary_assembly.fa -> ../fasta/Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.dna.primary_assembly.fa
│ └── ...
└── hg19
FAIR: guidelines proposed by the scientific community 1.
Objectives: promote best-practice tools to help produce and publish reproducible analyses throughout the data lifecycle.
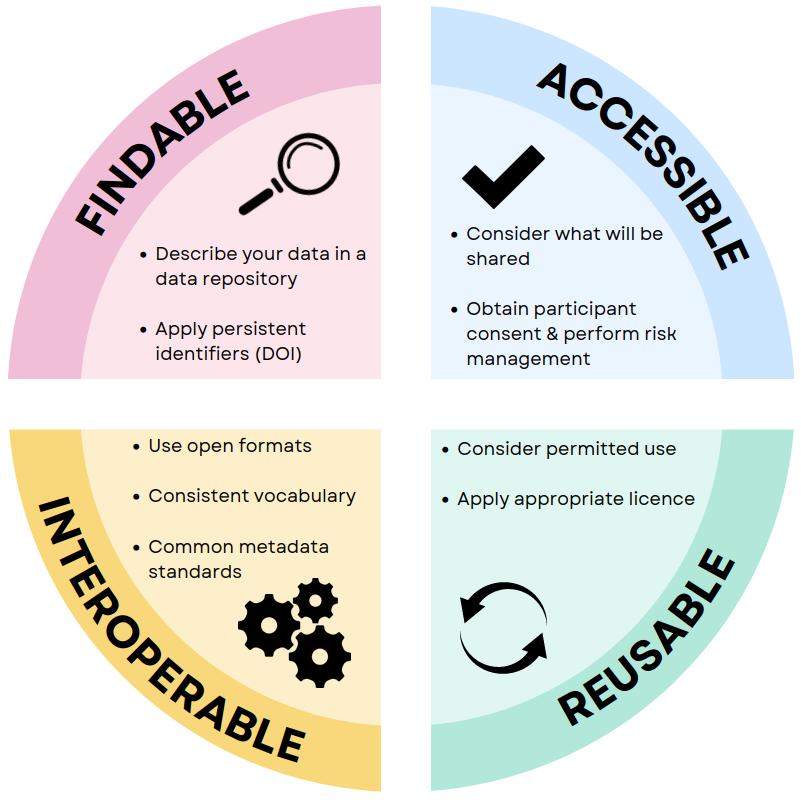
FAIR and DMP

Over 70% of researchers have tried to reproduce another scientist’s experiments without success, and over half have failed to reproduce their own experiments!
FAIR and DMP

FAIR and DMP
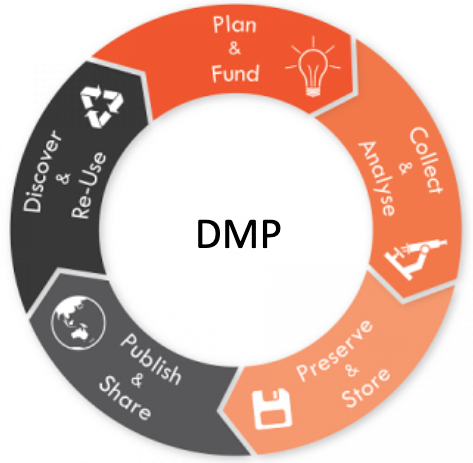
Figure from: https://www.universite-paris-saclay.fr/recherche/science-ouverte/les-donnees-de-la-recherche/introduction-aux-plans-de-gestion-de-donnees
FAIR and DMP
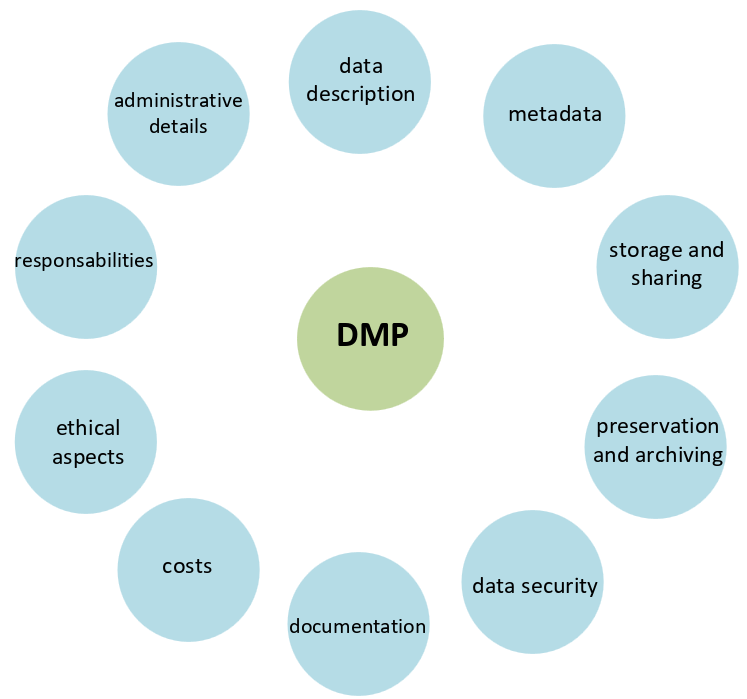
FAIR and DMP
Data life cycle
Very useful tools exist to collect, manage and share data and metadata over the time.
Data life cycle
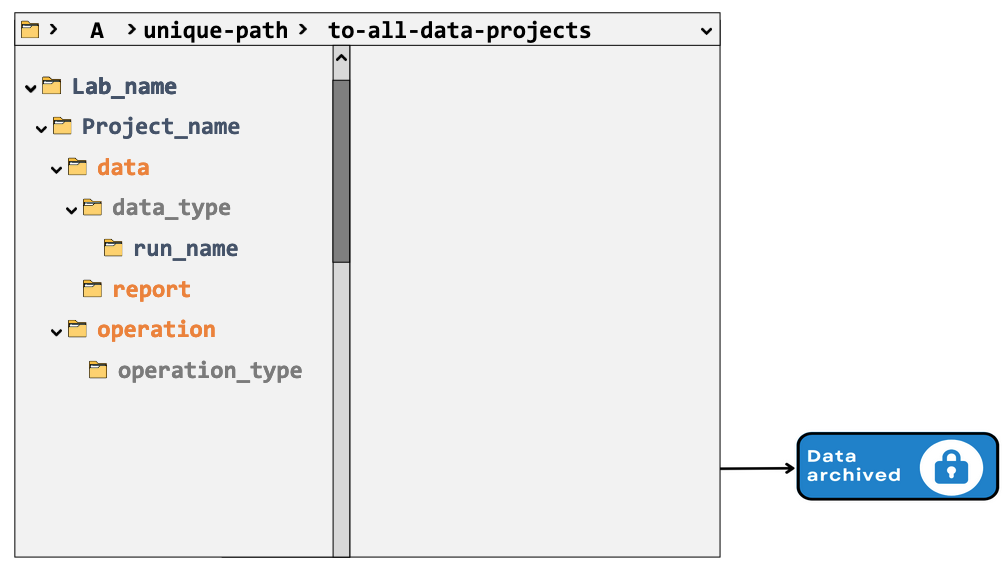
Data life cycle
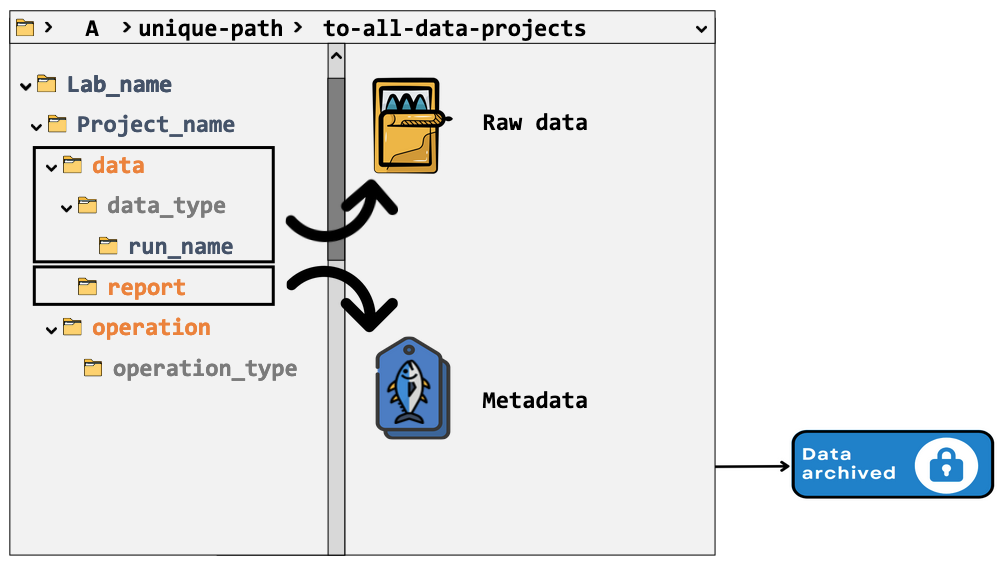
Note: ‘operation’ folder many contain particular final results, e.g. a sequence assembly.
Data life cycle

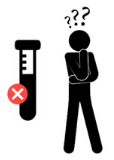

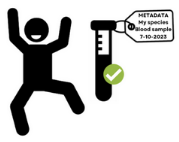
Data life cycle
Metadata 1 describes the data (main characteristics), such as author, creation date, content, format, associated project, associated sample, etc.
Given types of collected data, its description should be achieved using metadata standards, e.g. controlled vocaularies, ontologies, etc. Do not invent your own terms!

Data life cycle
Data has to be associated with a license that describes how data can be used by anyone.

As a French public research institute, we should use the ETALAB 1 public license from the Direction Interministérielle du Numérique (DINUM).

However, in practice: we should use the CC-BY license to be in an international legal framework. Not using CC-BY license prevents ENA submission.
Data life cycle
When it is time to publish your work, you will have to make your data accessible to everyone.
There are three major ways of doing that:
Data life cycle
Have in mind that:
As a consequence, it is very important to think about public data release at earlier stages of the project beacuse it is a very time consuming step.
DMP should be used to answer this question and provide appropriate solution(s).
Data life cycle
Ifremer Sextant Catalog of Oceanographic Data - CoreTrustSeal Certified
Data life cycle

Recherche Data Gouv 1 has been designed to support research teams in their work of structuring data to make it easy to find, accessible, interoperable and reusable - in other words, in line with the “FAIR” principles. These services are operated by INRAe.
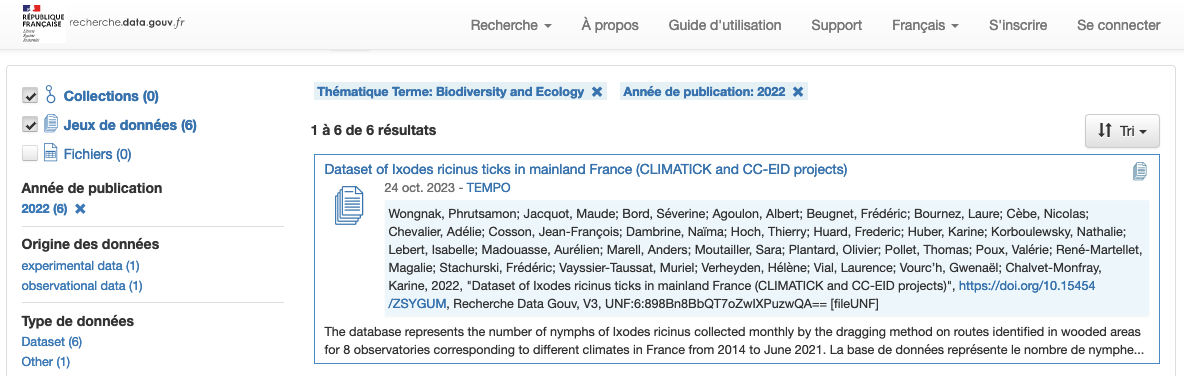
Data life cycle
Publish sequencing data to international databases for international referencing.

Data life cycle
There are a large numbers of services to publish and share data to the scientific community.
We cannot talk about everyone, so during this course we will take the example of submitting sequencing data.
For any other research domains, you may certainly benefits from (meta)data standards defined for these domains.
Following content will be:
Let’s consider we want to publish our sequencing data within the European Nucleotide Archive (ENA) databank managed by the European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI), Hinxton, UK.
You have to:
Collecting and sharing data and metadata
https://ena-docs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/submit/study.html
Collecting and sharing data and metadata
Collecting and sharing data and metadata
These are controlled vocabularies organized as a collection of scientific themes.


Collecting and sharing data and metadata
Ontologies are set of terms (along with unique IDs and description), each of them covering a particular scientific field and validated by scientific communities.
Ontologies are interoperable, logically well-defined, machine readable controlled vocabularies.
A few examples:
Collecting and sharing data and metadata
As of November 2023, there are about 40 ENA sample checklists:
Do not invent your terms to describe your metadata. Instead, use above one!
Collecting and sharing data and metadata
A possible solution can be to set up a spreadsheet document containing the many pieces of information (i.e. metadata) useful to describe your sequencing data.
Pros:
As soon as such a document is fully filled in, it must be locked against any further modification and stored next to raw data.
Collecting and sharing data and metadata
Here is an example of a spreadsheet-based document designed to collect metadata following ENA requirements 1:
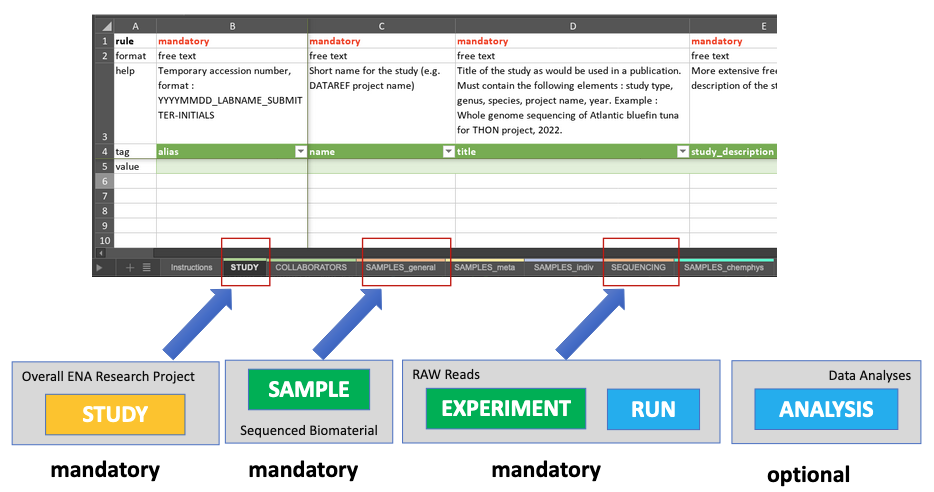
Collecting and sharing data and metadata

Collecting and sharing data and metadata
ENA allows submissions via three routes, each of which is appropriate for a different set of submission types. You may be required to use more than one in the process of submitting your data:
Pros of programmatic submission: standard code, automatic submission (limit errors of manual handling), possibility to run a dry submission (test).
Collecting and sharing data and metadata
Example of a catalog entry programmatically submitted to ENA:
Metadata related to ENA Study object
Collecting and sharing data and metadata
Tool to check FAIRness of your materials: FAIR-Checker
Example for the Nextflow-based pipeline SAMBA published on Elixir Workflowhub:
FAIRness evaluation